Java variables:
Data Types:
- int : int store integers values , such as 1,2,23,-21,56
- float: float stores floating-point values such as 1.2f ,2.3f ,4.6f;
- double: double stores floating-point values such as 1.2, 1.3, 4.6, 5.7
- boolean: boolean store true and false
General Rules for java variable:
- The identifier can be letters, digits, underscores, and dollar signs
- Identifier begins with a letter
- Identifier starts with a lowercase letter and it cannot contain whitespace
- The identifier also start with $ and _
- identifier are case sensitive ("value" and "Value" are different variables)
- Keywords, such as byte or int cannot be used as an identifier
Keywords in java:
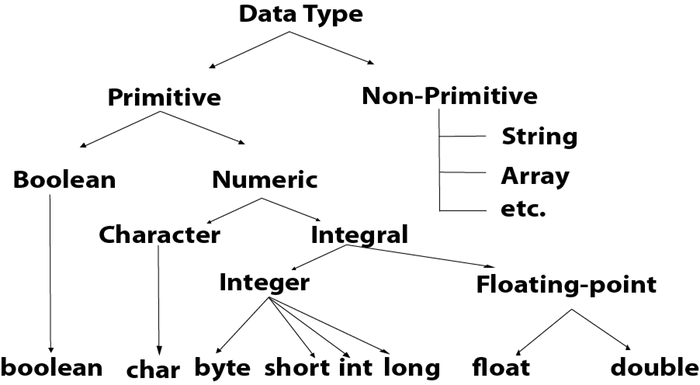
Data Types in java:
Video Lecture:
Syntax of Variables creation in java
<data type > <identifier> ;
Example:
public class Datatypes
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int integer = 10;
System.out.println(integer);
double floating_number = 1.9;
System.out.println(floating_number);
char character = 'A' ;
System.out.println(character);
boolean Good = true;
System.out.println(Good);
boolean Bad = false;
System.out.println(Bad);
short myshort = 12;
System.out.println(myshort);
long mylong = 2003030;
System.out.println(mylong);
float point = 34.54f;
System.out.println(point);
}
}
OUTPUT
10
1.9
A
true
false
12
2003030











0 Comments